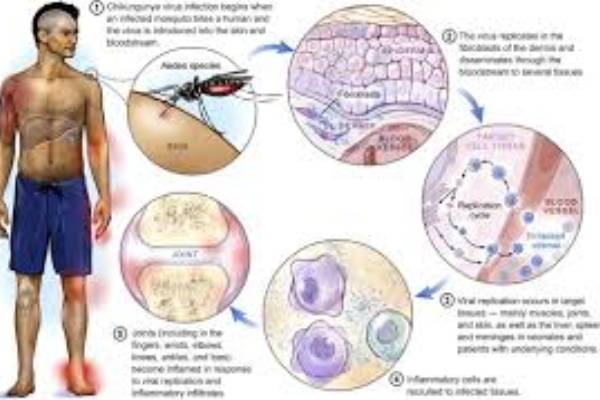
Chikungunya is a mosquito-borne illness that continues to spread globally, leaving patients with painful and sometimes long-lasting symptoms.
Here are the essentials:
1. How It Spreads
The virus is transmitted to humans through the bite of infected female Aedes mosquitoes — mainly Aedes aegypti and Aedes albopictus.
2. The Main Symptoms
Fever and severe joint pain are the hallmarks. Pain usually affects the wrists, ankles, hands, and feet. Other symptoms include headache, muscle aches, nausea, and skin rash.
3. How Serious Is It?
The disease is rarely fatal. However, the joint pain can be crippling, lasting weeks or even months, and may disrupt daily activities.
4. Is There a Cure?
No specific antiviral treatment exists. Care is focused on managing symptoms — using pain relievers, fever reducers, and anti-inflammatory medicines.
5. How to Prevent Infection
The best protection is preventing mosquito bites:
-
Apply insect repellent
-
Wear long-sleeved clothing
-
Sleep under mosquito nets
-
Eliminate standing water around homes
6. Where It’s Found
Chikungunya is widespread in Africa, Asia, and the Americas, and has recently appeared in parts of Europe.
7. What WHO Is Doing
The World Health Organization (WHO) monitors outbreaks, issues prevention guidance, and supports affected countries in controlling mosquito populations.
8. The Latest Situation
As of July 2025, the European Centre for Disease Prevention and Control (ECDC) reported more than 240,000 cases and 90 deaths worldwide, with outbreaks active in Africa, Asia, the Americas, and Europe.